Core Concepts
GenAI Editor
CodeCargo provides a powerful interface to edit your code with the help of our Expert Workflow Agent. Our agent specializes in working with all types of automations - GitHub Actions, GitLab CI Pipelines, Jenkins, etc. It also works well with secondary integrations used by pipelines such as infrastructure-as-code and Helm Charts. It can perform general code edits as well, but specializes in working with automations.
Workspace
Your workspace contains one (or more) files from one (or more) Git repositories. Any time you open the Editor, you are working within a workspace. You can use a single workspace for all of your edits, or you can open multiple workspaces. CodeCargo will save the state of your workspaces (including any code modifications) automatically. This means your changes will always be saved, even if you switch workspaces, logout, or go on vacation.
Understanding the User Interface
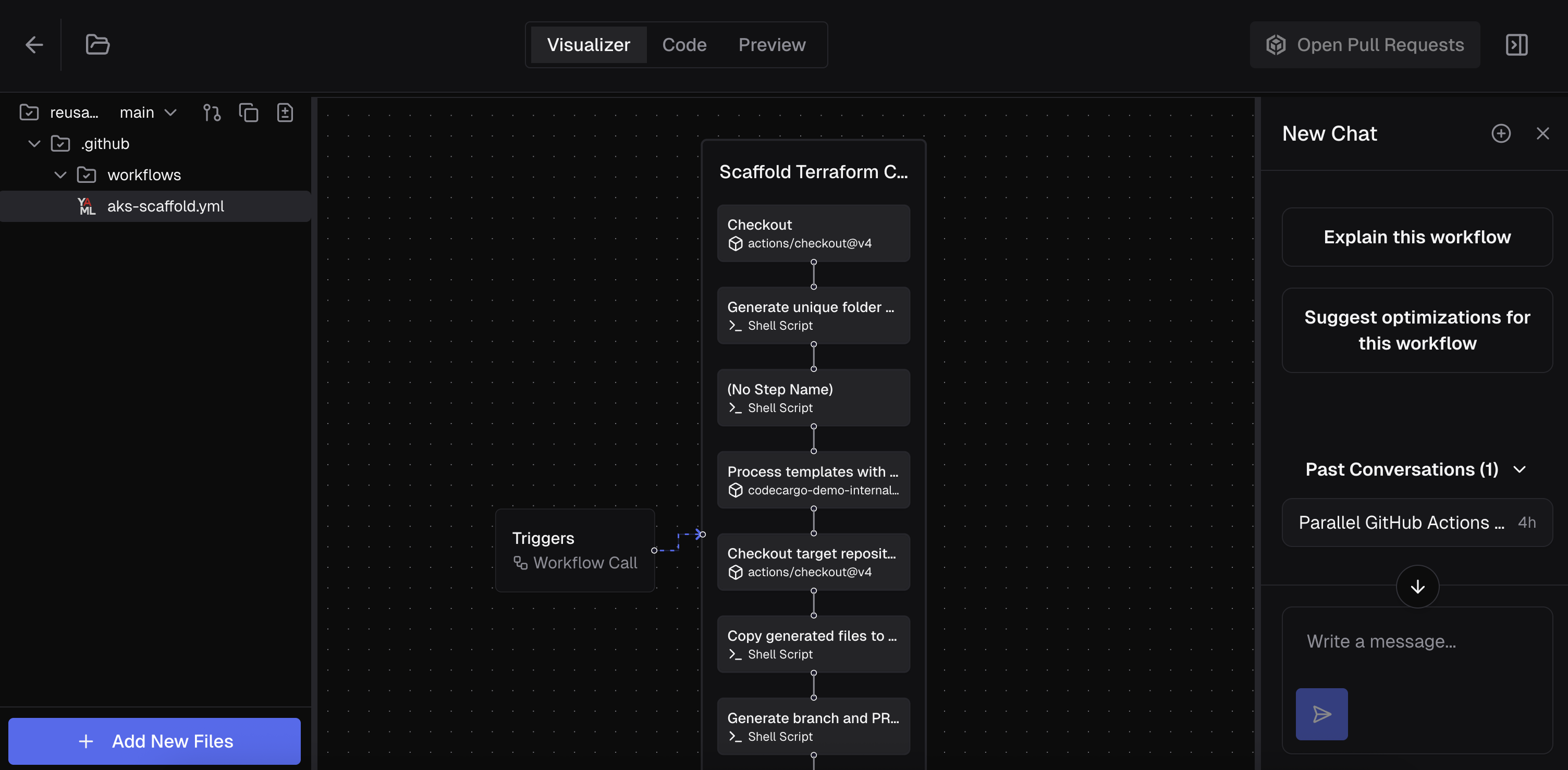
The GenAI Editor is a powerful interface to edit your code. The left side of the screen shows the files currently active in the Editor, for example, aks-scaffold.yml. For a file to become "active," you must have explicitly added it to your workspace or edited it.
The right side of the screen is the chat interface where you can talk to the Expert Workflow Agent.
The center of the screen has up to 3 views:
- Visualizer - shows GitHub Actions Workflows in visual form
- Code - code editor with multi-language syntax highlighting
- Preview - shows changes between the original and current state of the file (assuming edits were made)
Visualizer
The Visualizer currently works for GitHub Actions Workflows that contain jobs. It shows the different trigger events, jobs, and steps within each job. You can click on each of those for additional information.
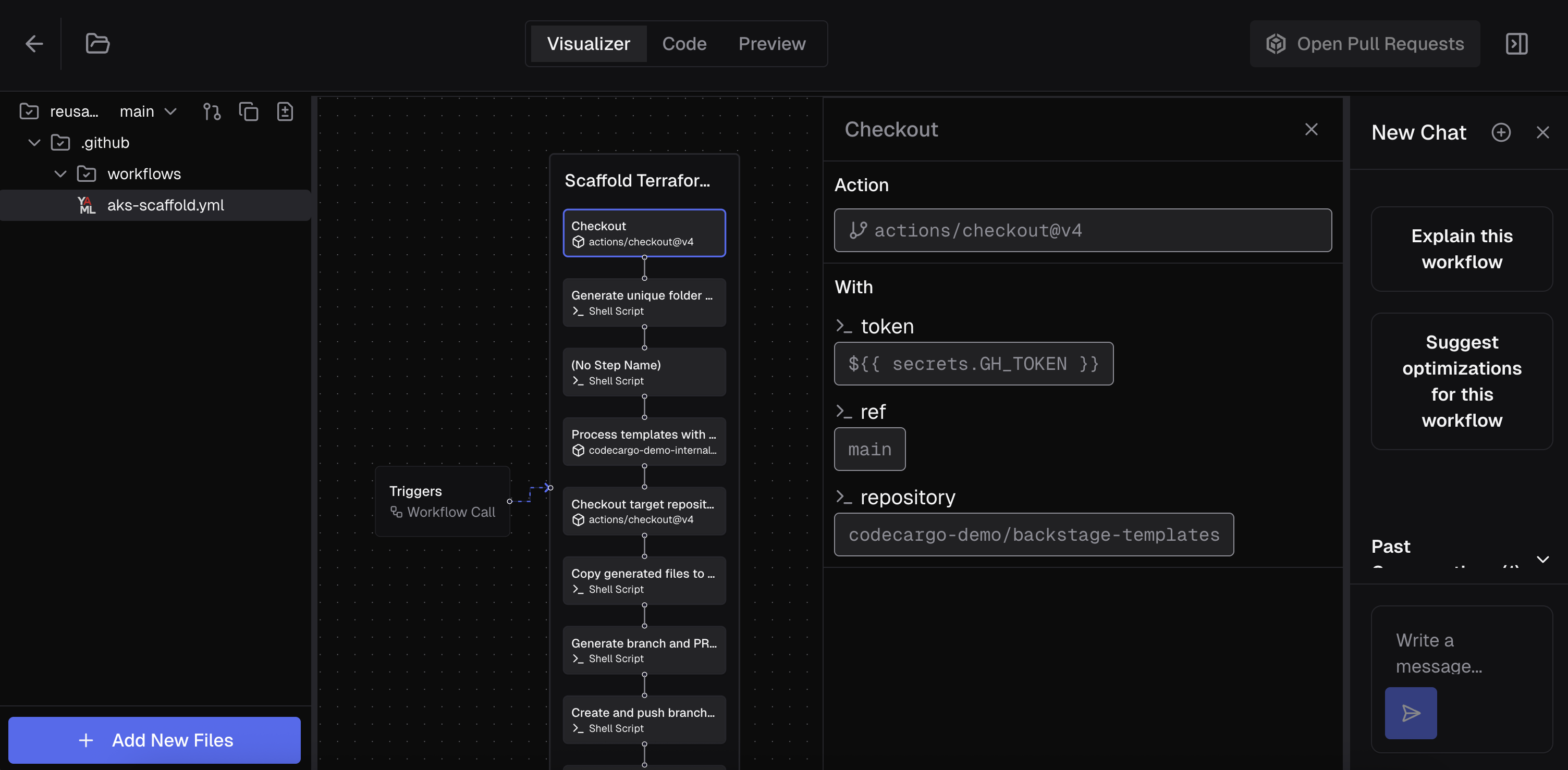
Code
The Code view is a simple editor that lets you view and update the current file. It includes syntax highlighting and hover details for built-in language specifications. You can edit the code of the underlying file here.
Preview
The Preview view will show you changes between the file's original and current state. This is very similar to the git diff view that you've seen in GitHub or other tools.
Open Pull Request
This button lets you open a pull request with your current changes. If you made changes to files across multiple repositories, it will create multiple pull requests. If you already created a pull request, you can make additional changes and use this button to push a new commit to the underlying branch for your pull request.
Note that you must have write permissions in the underlying GitHub repository to create the pull request.
Miscellaneous
The folder icon on the top left of the interface will collapse/expand the file explorer. The dashboard/arrow icon on the top right of the interface will collapse/expand the GenAI chat interface.
Context
When it comes to GenAI and editing files, context is everything. Within the editor, the Expert Workflow Agent has context specific to what you are viewing:
- Single File - the context includes that file + every other file on the
defaultbranch of the repository that contains the file - Multiple Files from 1 Repo - same as above, every single file in the repository
- Multiple Files from Multiple Repos - the context includes all open files + every other file on the
defaultbranches for every single repository that contains the files
To be more specific, if you open the editor with 2 files (repo-scaffold.yml in the repository reusable-workflows and create-azure-vm.yml in the repository iac-azure), then the GenAI agent will load every single file from the reusable-workflows and iac-azure repositories in context.
This allows you to directly edit or have the GenAI agent edit files in multiple repositories at the same time (e.g., your company just bought a new CVE scanner and you want to add its GitHub Action to every workflow that builds software in multiple repositories). You can also ask the AI agent to "take the best-practices from repo-scaffold.yml and apply them to create-azure-vm.yml" and plenty of other things.
Editing Files
Launching the Editor
To edit a file, you must open the GenAI Editor with one or more files. To add files to the editor, navigate to Building Blocks and select one (or more) workflows that you'd like to edit. Then click "Add X to Editor." Alternatively, you can just click "Open Editor" and follow prompts on the screen to add files.
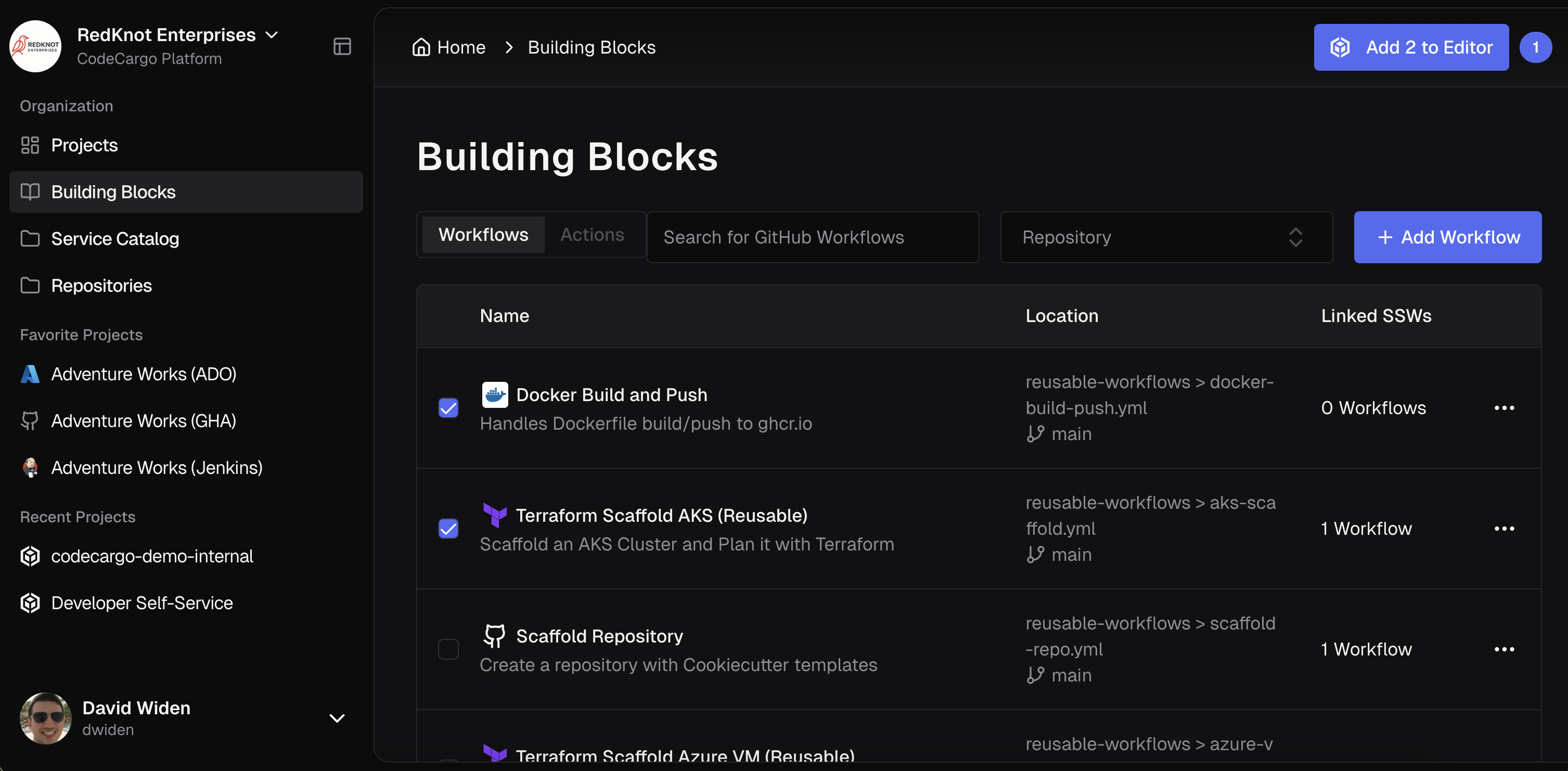
Whenever you change a file in the Editor, CodeCargo will create a Workspace. These preserve the state of your modified files so you can work with them over time or create pull requests.
If you have any active Workspaces, the "Open Editor" button will have a badge indicating how many Workspaces you have opened. If you do not select any files and click "Open Editor," it will open your most recent Workspace. Alternatively, if you select one (or more) files by checking them, then click "Add X to Editor," you will have a brand new Workspace with those files open.
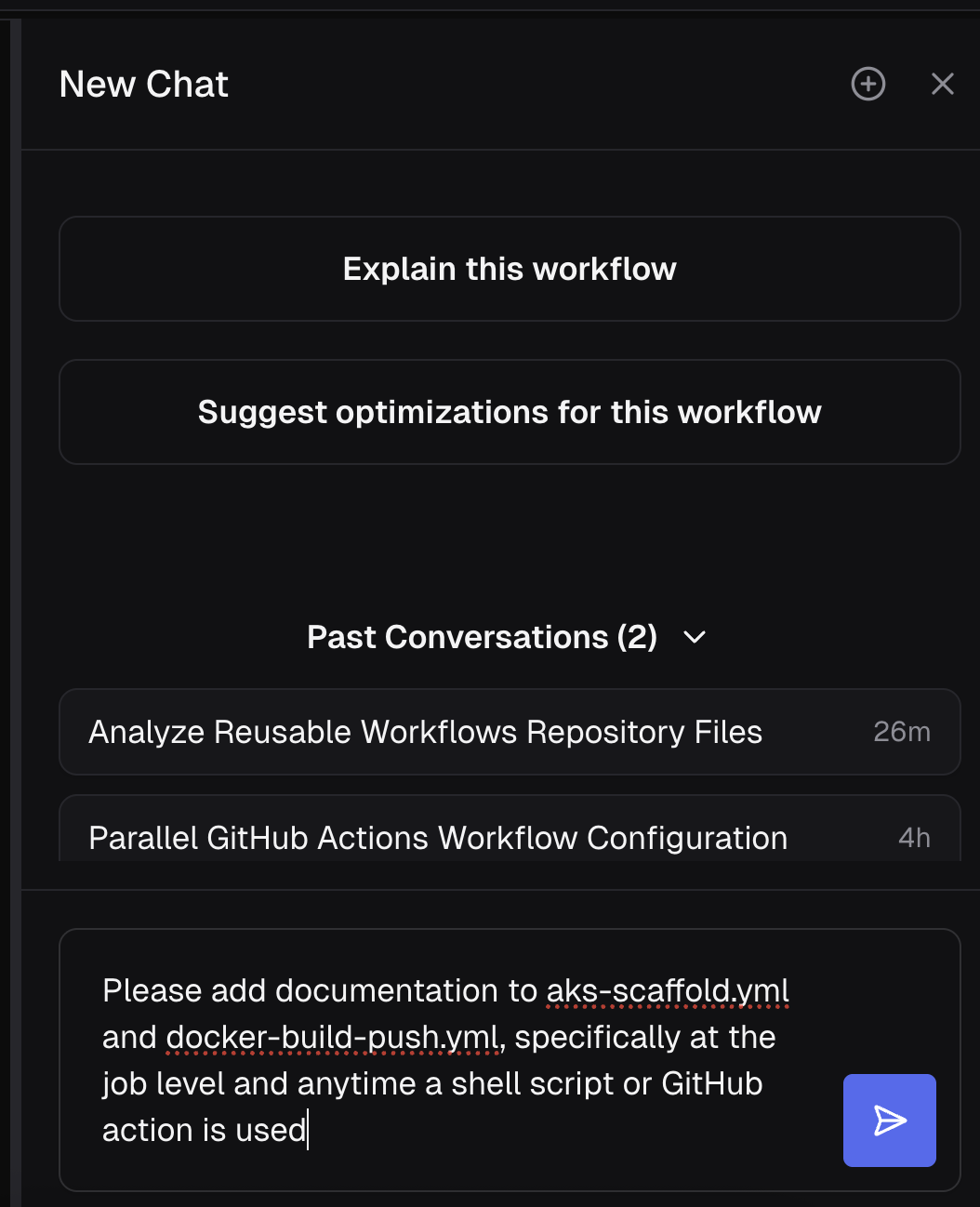
Editing Files with AI
To edit your files with our Expert Workflow Agent, simply talk to the agent and tell it what you'd like to do. You can ask it questions, give it instructions, or even make it develop a plan before you want it to run. Here's a sample prompt:
After you ask a question, the Expert Workflow Agent will provide simple answers as necessary (e.g., if you ask "how may files are in this repository," it might reply "215."), show tool calls, and provide a task list for complex actions. Here is an example of output from the above prompt:
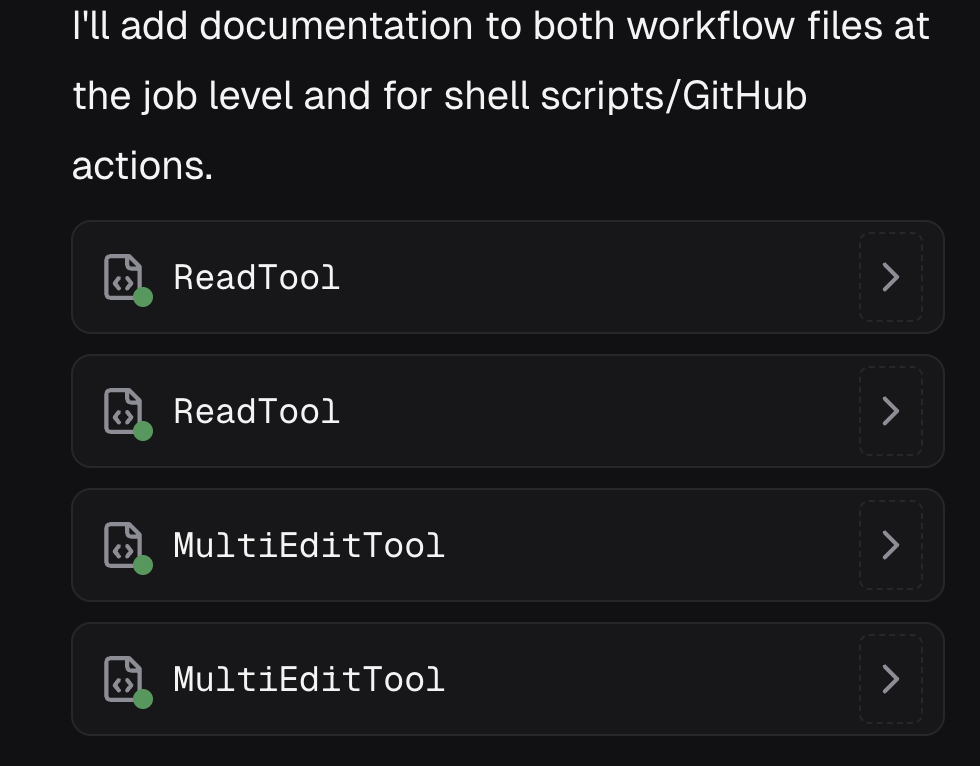
In particular, our agent ran several tools to read then write to files. Then it updated the files and explained what it did. Go to the Code tab to accept/reject the changes. To view the changes made to the file, navigate to the Preview tab at the top of the page.
Whenever you (or the AI) makes an edit to a file, there will be an "M" badge to the right of the filename in the file explorer on the left side of the screen.
Once you ask the Expert Workflow Agent to update one (or more) files, you can view the changes in both the Code and Preview views in the middle of the UI. You can accept the changes in the Code view. Once you accept the changes, highlighting will disappear in the Code view but changes will remain in the Preview view to show you all modifications between the original and current state of the file.
Workspaces
Whenever you open the editor, you are working within a Workspace. Workspaces keep track of your current modifications and are preserved even if you exit the editor page. Workspaces are similar to a local working branch on your developer laptop. You can have multiple Workspaces associated with your account at any time.
Create a New Workspace
To create a new Workspace, select the files that you want to edit and then open the editor. Any changes you make will be saved in the new Workspace.
Saving a Workspace
Any changes that you directly make (or that you accept from the AI) are automatically saved. These changes will be preserved if you exit the editor or even logout of CodeCargo.
Use an Existing Workspace
If you previously edited files that are now saved in an existing Workspace, you can open the editor based on that pre-existing Workspace. To do so, click the numbered badge directly to the right of "Open Editor," click the down chevron on the Workspace you'd like to be active, click "make active," and then finally open the editor.
Creating Pull Requests
Once you are done making edits to the files within your Workspace, you can push the changes to GitHub by creating a Pull Request. Click the "Open Pull Request" button - this will open a menu that lets you create the PR.
Create a New PR
If your Workspace contains new changes, CodeCargo will create a new Pull Request for you. Click the button "Open New PR," follow the on-screen instructions, and you'll see the PR in GitHub.
Edit an Existing PR
If you are making an edit to files in a Workspace where you've already created a Pull Request, cliking the "Open Pull Request" button will let you push changes to the underlying GitHub branch that the PR references. This lets you provide new changes to an existing PR.
Note you can only push changes to the underlying branch of a Pull Request that you've created in CodeCargo
Complex Changes
There may be situations where you want to create new and edit existing Pull Requests from your Workspace. For example, you may have added a file to your Workspace, edited it, created a Pull Request, then added a new file to your Workspace, then edited both files.
In that scenario, you can edit an existing Pull Request (the first time) and create a new Pull Request (the second file). CodeCargo will seamlessly handle this for you. After you click the "Open Pull Request" button, the UI will explain what action will be taken for each change.
Sample Queries / Ideas
CodeCargo's Expert Workflow Agent is incredibly powerful. Combined with the ability to make bulk modifications to across multiple repositories, Here are a few things you can do with it:
- Convert your Azure DevOps (or other) pipeline into a GitHub Actions Workflow
- Create a brand new GitHub Actions Workflow
- Enforce industry standard best-practices to your GitHub Actions Workflow
- Perform bulk upgrades across repositories within your codebase
- Update a reusable workflow's inputs, then update every invocation with those new inputs
